General Urology in Cleveland TN
Here at Tennessee Valley Urology Center, we specialize in all General Urology conditions affecting adult men and women. General Urology in Cleveland TN is a specialty of medicine concerned with the function and disorders of the urinary system of both men and women, and the reproductive system of men.
Are you experiencing painful, uncomfortable or embarrassing symptoms? We help our patients to get the support they need to restore their urological health and wellbeing.
Contact us today for an appointment.
We offer expert care for the 7 key urological conditions that affect both men and women
Our Urology experts offer a range of procedures to treat patients and their personal needs
If you are worried about your symptoms, talk to us today.
Read more about specific urological conditions and procedures at:
How Our Urinary System Works - A Quick Reminder
The urinary system is responsible for urine formation and excretion. Kidneys produce, store, and excrete urine as a waster product from blood, which funnels through ureters and fills the bladder. When urine is filled to the upper limit of the bladder, a person feels the urge to urinate.
When you pee, the pelvic floor muscles relax, opening the gateway to the urethra creating a urine flow out of the bladder. The detrusor(bladder) muscle contracts to empty the bladder almost simultaneously. This muscle also maintains pressure so that the bladder is emptied.
General Urological Problems
As adults, men and women can experience several common urological problems such as kidney stones, hematuria (blood in urine), bladder incontinence, an overactive bladder, or urinary tract infections (UTIs). Our specialist team also treats urological cancers affecting the kidneys or bladder. We help patients with cancers affecting the prostate, testicles, and penis, detailed under the Male Urology section.

General Urological Solutions
Many treatment options are available for patients to manage their general urological problems. These range from:
- Medication: Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, hormone creams.
- In-office Procedures: Vasectomy, Prostate biopsy
- Surgeries: Lithotripsy, circumcision, prostatectomy, just to name a few
- Robotic Surgery : One of the many technological advances that has become commonplace in this field.
Be Confident in the Quality of Care We Provide At Tennessee Valley Urology Center
Here We Have Discussed Seven General Urological Conditions
Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that lodge in the kidney, ureters, or urethra. Depending on their size, they can be extremely painful and, in some cases, dangerous. However, when they’re smaller, they can also go unnoticed and pass out in the urine.
Your doctor may use different names to refer to kidney stones, such as renal calculi, nephrolithiasis, or urolithiasis.
Some kidney stones stay within the kidney and do not cause any issues. If the stone is able to reach the bladder, it can typically be passed through urine out of the body. In some instances, stones can become lodged in the ureter from the kidney and can cause pain.
Although kidney stones often pass without any further injury to the patient, in serious cases they can cause sepsis and even death. This is because larger stones can block the ureters, which prevents the urine from exiting the kidney. The kidney can then become infected, or the body might progress into sepsis, an infection response which can cause long term poor health or even be fatal in some cases.
Kidney Stone Symptoms
The symptoms of a kidney stone include:
- Pain in the lower back, which can manifest on either side
- A subtler pain that emanates originates from the stomach area
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever or chills
- A change to the smell of the patient’s urine, and a foggy appearance
- Signs of blood in the urine
2 Most Common Types of Kidney Stones
Calcium Oxalate
80% of kidney stone cases are known as calcium oxalate stones. There are two types of calcium stones: calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate. Calcium oxalate is the most common of the two. Some individuals have too much calcium within their urine, therefore increasing the likelihood of calcium stones.
Uric Acid Stones
The uric acid kidney stone is the second most common form of stones. Uric acid is a waste product that comes from chemical changes within the body. Conditions such as type 2 diabetes, being overweight, gout, and a diet that is too high in animal protein and too low in fruits and vegetables may promote formation of uric acid stones.
Less common types of kidney stones are struvite stones and cystine stones, caused by upper urinary tract infections or cystinuria respectively.
Hematuria (Blood in the Urine)
Hematuria is another way of saying “blood in the urine.” This can be categorized under “gross” or “visible” hematuria. Other times there is blood in the urine that is not seen by the visible eye, this is called “microscopic” hematuria.
Blood in urine can come from anywhere in the urinary tract including the kidneys, bladder, or urethra. The causes of hematuria in all of these locations are varied and can be harmless or very serious.

Causes of Hematuria
There are many reasons you may have blood in your urine. When blood is found in the urine healthcare providers want to be sure that there is not a serious health concern involved. Your urology doctor will want to examine you and review the risks of cancer or other non-cancer causes for the blood in the urine such as a UTI, kidney stone, or trauma. Other testing could be necessary to diagnose the cause of hematuria. Here are some of the more common causes:
- Urinary Infection (UTI)
- Enlarged Prostate
- Prostate Infection
- Kidney trauma
- Kidney disease
- Bladder cancer
- Kidney cancer
- Kidney stones
Bladder Incontinence
Incontinence is one of the more common and embarrassing conditions in urology. Many men and women suffer from urinary incontinence. The brain and the bladder both control urinary function. The bladder stores the urine until you are ready to empty it. Once you are ready to empty your bladder, the brain sends a signal to the bladder, and the muscles contract to do so.
Your doctor will discuss your medical history including any hereditary factors and conduct some tests as part of a physical examination. Tests could include a cough test (to see if a urine leak occurs), a urine sample dipstick test (which can determine if the problems are related to a urinary tract infection), or a residual urine test using an ultrasound or a catheter. There are also gender-specific tests requiring physical examinations to test the prostate gland (men) or strength of the pelvic floor (women). Bladder incontinence is categorized into four groups:
Stress Incontinence
Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) can happen when movement such as laughing, coughing, sneezing, or running puts pressure on the bladder causing it to leak urine. It is more common in women than in men.
Overflow Incontinence
In having overflow incontinence, the body produces more urine than the bladder can hold causing it to leak urine. Frequency or “dribbling” are both symptoms of overflow incontinence. This is more common in men with prostate issues or a history of prostate surgery.
Overactive Bladder
OAB, also known as “urge” incontinence is known to restrict one’s ability to perform normal life activities. With OAB, the brain tells the bladder to empty even if it is not full. The main symptom of an overactive bladder is the urge to urinate right away.
Mixed Incontinence
Mixed incontinence is the mixture of both SUI and overactive bladder. Some individuals will experience SUI during activity and feel the urge to urinate.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) occur when bacteria get into the urine and makes it’s way to the bladder. When a UTI is present, the lining of the bladder and urethra can become irritated. This irritation can cause pain to the lower back and make you feel as though you have to urinate even when there is not much urine in your bladder. Other symptoms of a UTI could be cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is common in both men and women. However, it is more common in women due to the shorter length of the female urethra, which makes the female urinary tract more vulnerable to bacteria.

Most Common UTI Symptoms
Symptoms of a UTI will vary from one person to the next, but typically include:
- Pain or burning while urinating
- Feeling the frequent urge for urination
- The need to urinate despite having an empty bladder
- Blood in urine
- Pressure or cramping in the groin or lower abdomen
Getting a Quick Diagnosis
Urinary Tract Infections can be diagnosed by a urine sample. The urine is examined under a microscope for bacteria or white blood cells, which are both signs of an infection. A urine culture can also be taken from the urine provided that identifies the type of bacteria in the urine that could be causing the infection.
After Treatment
Many symptoms of a urinary tract infection fade within a few days of taking an oral antibiotic. If all symptoms of a UTI have gone away after the antibiotic is completed, then another urine test would not be needed to ensure infection is gone.
If you get more than three UTI’s a year, then you should contact your healthcare provider for an appointment. Furthering testing could be needed to find out why infections are recurring.

Interstitial Cystitis (IC) ~ Painful Bladder Syndrome
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a poorly understood condition characterized by chronic recurrent pain or pressure in the bladder or pelvic area. It’s often known as painful bladder syndrome or bladder pain syndrome without an infection or other cause.
IC is also associated with sudden strong urges to urinate as well as more frequent urination. Some women may experience pain when having sex. Symptoms resemble that of a UTI but for some, symptoms never go away while others symptoms come and go.
Treating IC
Unfortunately, the cause of IC is as yet unknown, and it cannot be treated by using antibiotics. Usually IC is treated on a case to case basis depending on the symptoms of the patient. Options for the treatment of IC are limited and are designed to help improve symptoms. They include:

Dietary Intervention
Dietary change is the first recommendation made when IC is diagnosed. Generally, patients are encouraged to avoid certain foods and drinks, such as alcohol, citrus fruits or their juices, chillies, onions, coffee or tea, chocolate, milkshakes, coffee, cranberries or their juice, soda or sugary drinks, tomatoes or their juice, and electrolytic drinks.
Lifestyle Intervention
Having a more relaxed and healthy lifestyle can help with IC symptom management. It includes quitting smoking and reducing stress with strategies like meditation.
Surgical or Procedural Intervention
There are also several surgical options for IC. It includes bladder augmentation (surgically increasing the size of the bladder), cauterization (closing ulcers in the bladder by using an electrical current or laser), Botox injections (relaxes the bladder), or neuromodulation (electrical nerve stimulation using a device that is implanted).
We offer the Best Advice and Treatment Plans for your Urology Complaints
Read more to understand the 8 most common diagnostic procedures at our Cleveland office
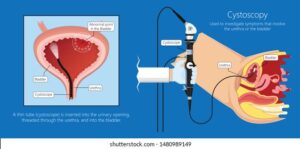
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is a minimally-invasive diagnostic procedure that uses a cystoscope to examine inside your bladder and urethra visually. A cystoscope is a thin, lighted tube with a tiny camera attached. It lets your doctor look at your bladder from inside to check for injuries, bleeding, narrowing, or blockages of the urinary passage and other abnormalities.
Why have a Cystoscopy?
A cystoscopy may be recommended as a diagnostic test to investigate the reason why you are experiencing:
- Recurring urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Painful urination
- Suspected bladder stones
- Urinary incontinence
- Urinary retention
- Hematuria
What to Expect During the Cystoscopy
The cystoscopy is performed in our offices and typically takes around 10 minutes. A numbing gel is usually applied to reduce discomfort when inserting the cystoscope. The procedure can be a little uncomfortable rather than painful. If a biopsy is needed, local anesthesia may be used to numb the area before a tissue sample is taken.
You will need to provide a urine sample to confirm you don’t have a current UTI. Otherwise, the doctor may need to cancel and re-schedule the procedure.
Recovery from a Cystoscopy
As it is a minimally invasive procedure, recovery is very quick. You’ll most likely be prescribed antibiotics to prevent infection.
The procedure risks are very low; however, you may experience temporary discomfort or difficulty with urination.
Urodynamics Diagnostic Procedure
Urodynamics (UDS) test is a diagnostic procedure that allows your Urologist to evaluate the function of the bladder, urethra, and sphincters. Specifically, the test evaluates how well they hold and release urine and identifies blockages or leaks. Your doctor may request a urodynamics test to investigate the following general urology issues:
- Urine leakage
- Frequent trips to the bathroom
- Pain while urinating
- Sudden urge to urinate
- Trouble releasing urine
- Inability to fully empty the bladder
- Repeated urinary tract infections
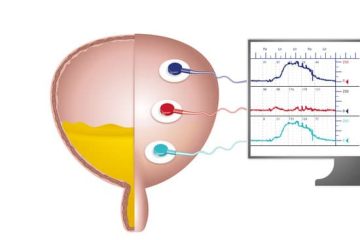
What to Expect from a Urodynamics Test
This procedure is minimally-invasive and involves inserting a small pressure sensor into the bladder and either the rectum or vagina. The test will generally last about 20 to 30 minutes, and you will be asked to both hold urine while the bladder is filled and release urine when instructed. Often you are asked to perform actions such as straining or coughing to allow the technician to test for incontinence. Because a catheter is inserted, there is a small risk of urinary infection or discomfort with urination after the procedure.
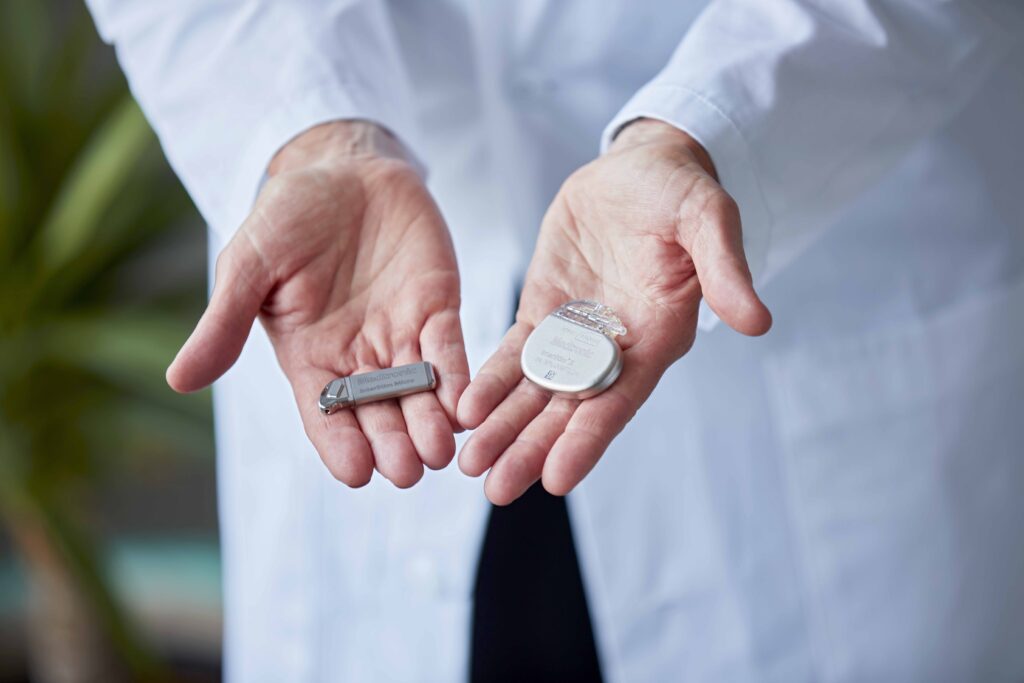

InterStim - Treatment for Urinary Incontinence
InterStim therapy is a treatment for refractory overactive bladder, incontinence, and urinary treatment. This therapy is used when the first and second line of treatments fail. The treatment consists of mild electric pulses to stimulate the sacral nerves above the tailbone, near the spinal cord, at the sacrum. Your doctor might call this sacral neuromodulation, and the affected nerves are called the sacral nerve plexus.
The InterStim device is an implantable pulse generator placed in the lower back during surgery. Because it is implanted, the success of the procedure must be tested first, for about a week, before the InterStim is implanted for a long term. It will give your doctor a chance to test if the procedure helps improve your incontinence.
InterStim Testing
The procedure for whether the InterStim therapy is working is known as InterStim testing. Before the test unit is implanted, you will be asked to keep a detailed diary of your urinary episodes for several days so that a comparison can be made to your bladder function during the testing phase.
The first test usually takes longer than an hour, including prep time and post-procedural instructions. At the start of the test, you will lie face down on the examination table, and your lower back will be numbed. Your doctor will then put two temporary wires (white wires, aka electrodes) into your lower back, one on the right and one on the left side of the sacrum (tail bone).
During the first test, your doctor will send electrical pulses through each wire and ask you to describe where you experience a physical sensation. This is done to confirm that the wires are in the right place. If it is the right place, you will experience a sensation in the perineum, the bicycle area between the legs. This sensation will feel like a light pressure, tingling, or fluttering.
After your doctor is satisfied with placing the wires, you will be given a little adjustable electrical box, called an external pulse generator, to connect to each of the wires at home. You will then trial the pulse generator for a week to see if it helps you. In the first part of the week, you will need to connect the box to just one wire and record any changes in your urinary patterns. You can use the other wire for the remainder of the week and record your urinary patterns.
If the test is successful, your doctor will recommend the InterStim implant.
PTNS - for Overactive Bladder (OAB)
Urgent PC is a different neuromodulation therapy that targets the percutaneous tibial nerve. Urgent PC Neuromodulation System is a non-drug outpatient treatment for overactive bladder-associated symptoms, including urgency, frequency, and urge incontinence. This procedure has been proven effective for those with urgent urinary symptoms.
Your doctor will have you seated comfortably in the office, where the nurse can easily insert a slim needle electrode near your ankle. This electrode is connected to a device that releases electrical impulses along the tibial nerve, which will travel up to the nerves in the leg that will go further to the nerves that control the bladder.
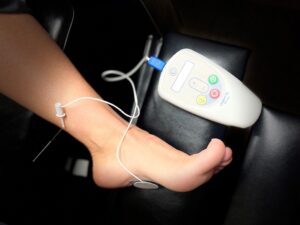
Patients will usually feel a mild sensation in the foot or leg during this treatment. These sessions will typically last 30 minutes and can be done weekly for 6 to 12 weeks. It could take up to 6 weeks to see changes in your urinary urgency. It is important to note that each patient responds differently. Therefore follow-up appointments will be necessary to monitor your symptoms and perform necessary maintenance treatments.
Many studies show that up to 80% of patients improve using Urgent PC treatment. This treatment can also be used alongside other bladder control treatments if your physician sees it necessary.

Bladder Botox
Bladder Botox is used to control urge incontinence, a form of incontinence that is also known as overactive bladder (OAB). The Botox that your doctor will use on your bladder is the same as the Botox used for cosmetic procedures.
Botox is the short name of a neurotoxic protein called botulinum toxin that is produced by a bacteria (Clostridium botulinum). Botox is injected into the specific site and blocks the nerve function in the bladder musculature. It causes the muscle cells around the bladder to stop squeezing, which reduces bladder overactivity. It also allows the bladder to fill more completely and gives you more time between visits to the bathroom.
What to Expect During Treatment
Bladder Botox is administered as an outpatient procedure in our Cleveland or Athens offices. Your doctor will administer a pain-numbing medicine and then insert a cystoscope which is a lighted instrument that passes down the urethra into the bladder. When the cystoscope reaches the bladder, injections are made in several sites around the bladder wall. The entire procedure takes about 10 minutes.
Results and Side Effects
Bladder Botox is very successful for many people, but not all. The positive effects of this procedure can last for several months and up to a year. After this time you will need to seek follow-up treatment. All procedures have associated risks, so whilst very rare, this procedure could result in:
- Development of a urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Painful or difficult urination (dysuria)
- Urinary retention
- Hematuria
Specialist Urology Procedures
Robotic-assisted Urologic Surgery
Robotic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical approach to perform complex urologic procedures. In urology, this technology is used to treat prostate cancer and kidney cancer, as well as many non-cancerous conditions of the kidneys, bladder, and prostate.
Robotic surgery uses several small incisions (each about 1/2 an inch) to gain access to the body cavity. The robot creates an enlarged field of vision to allow for excellent precision and control. Robotic surgery has been used in urology for over 20 years. The technology has evolved over time and continues to grow.
What are the benefits?
Robotic surgery offers many advantages to patients. These include:
- Smaller incisions than conventional open surgery
- Potential for reduced pain
- Potential for less blood loss and fewer blood transfusions
- Potential for quicker recovery time
How do I know robotic surgery is for me?
Dr. Box is our robotics expert at Tennessee Valley Urology. He advocates for the benefits of robotic urologic surgery to improve the patient experience and surgical outcomes.
Robotic surgery may not be suitable for everyone, so be sure to talk to your doctor about the surgical options that are right for you.
TVUC ~ The Best Urology Doctors for Helping Solve Your General Urology Issues
Our highly skilled, board-certified Urologists are the leading doctors across the Tennessee Valley. Call Tennessee Valley Urology Center today to book your appointment and visit us at our Cleveland or Athens offices. We are available for a warm and reassuring discussion to understand your symptoms so we can offer personalized treatment plans to get you back to good urological health.
Helping Patients In and Around Cleveland TN
- Benton
- Hopewell
- McDonald
- Ocoee
- Ooltewah
- Reliance
- Snow Hill
- South Cleveland
- Wildwood Lake
Supporting Patients In and Around Athens TN
- Decatur
- Etowah
- Madisonville
- Niota
- Riceville
- Sweetwater
- Williamsburg
Treating Patients In and Around Copper Basin & GA, NC Border Towns
- Ducktown
- Harbuck
- Wildwater
- Blue Ridge
- Mccaysville
- Murphy