Treatments for Bladder Incontinence in Cleveland TN
Suffering from bladder incontinence in Cleveland TN? Bladder incontinence is a common condition in urology, affecting both men and women. Understandably, it can be embarrassing, stressful and cause anxiety.
Our urology doctors will discuss the treatment options available with sensitivity, helping you manage or overcome this condition. Our team is highly experienced in making you feel at ease and getting you the help you need.
Urinary Incontinence is a Real Inconvenience!
Bladder Incontinence in Cleveland TN is when there is reduced control of bladder function. It commonly affects both men and women over the age of 40 but it is more common in women. A person with an overactive bladder has a weak or poorly coordinated bladder muscle, which causes them to urinate frequently — much more often than normal. Common risk factors for urinary incontinence can include advancing age, obesity, or women who have experienced natural childbirth. Urinary incontinence or overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) is one of the most common types of urinary incontinence, affecting millions of people yearly in the United States. There are 4 main types of bladder incontinence.
The Treatments for a Leaky Bladder
The good news is there are many treatments for a leaky or over-active bladder. The treatment that will be best for you will depend on the type of incontinence. Discuss your specific circumstances with our urology specialist to define a personalized treatment plan.
Urinary Incontinence is a Real Inconvenience!

Self-Managed Therapies
These involve behavior modifications and pelvic floor exercises. Pelvic floor exercises, called kegels, are used to strengthen the pelvic floor muscle, improve pelvic alignment and empower bladder control. Behavioral modifications for addressing leaking urine can involve:
- Reducing or eliminating bladder irritants from your diet (e.g. coffee, carbonated drinks, citrus juices)
- Timed urination (practicing control)
- A strict fluid intake regime
- Reducing your weight, especially in case of obesity
Medication
Drug therapies may include oral and topical treatments:
- Oral therapies include anticholinergics, selective alpha-blockers (mainly for men), and mirabegron (Myrbetriq) are used for urge incontinence
- Topical estrogen can be applied to the vaginal area for post-menopausal women
Innovative and Advanced Therapies for Urge Incontinence
There are a number of newer and innovative treatments that can help patients to manage or overcome the symptoms of overactive bladder. Discuss with your urology specialist of these are appropriate treatment options for your situation.
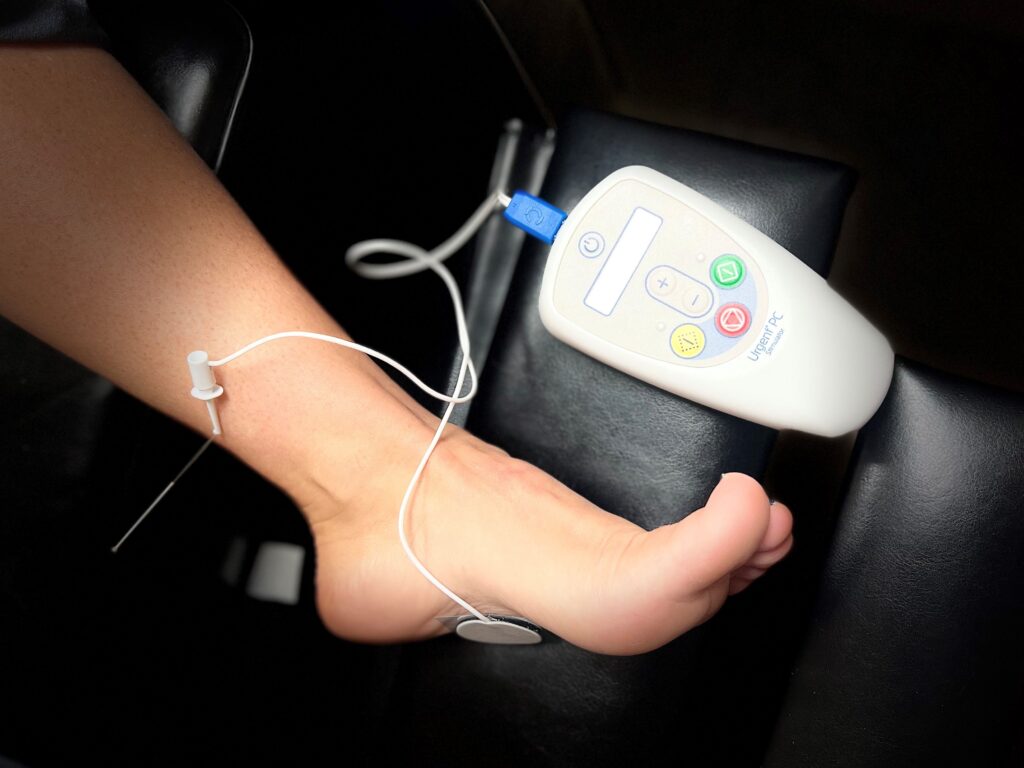
Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS)
PTNS involves weekly 30 min treatments given in the office that may continue for 2-3 months. During these procedures, a small needle is inserted into the ankle area and a weak electrical impulse is delivered.
Sacral neuromodulation (SNM)
SNM involves non-invasively stimulating the sacral nerve with a weak electrical current delivered by electrodes, effectively acting as a bladder pacemaker. The procedure is typically done in the operating room in two stages. The first stage is a trial to see if it improves symptoms. If the therapy works, then the electrodes are placed internally during an outpatient procedure.

Bladder Botox
Botox involves injection of medication into the bladder using a special camera or scope that is placed in the bladder through the urethra. This can be done in the office or as an outpatient procedure.
Surgical Procedures for Stress Incontinence
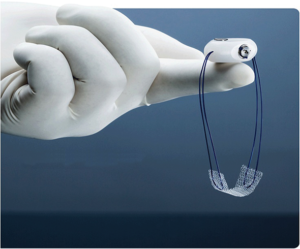
There are a variety of surgical methods that can be effective for stress incontinence. Here we outline some of those we offer at Tennessee Valley Urology Center. Contact us to find out more information.

Bladder Sling
A sling is a small piece of mesh that is placed around the urethra. This is done as an outpatient procedure.
Bulking Agent
A urethral bulking agent, primarily used for women, can be injected into the wall of the urethra to tighten the urethra against the flow of urine.
Artificial Urinary Sphincter
An artificial urinary sphincter (AUS) is a surgical implant that is placed around the urethra, mainly for men who have stress incontinence. A pump is placed in the scrotum and this controls the opening and closing of the urethra.
Types of Urinary Incontinence
There are a variety of surgical methods that can be effective for stress incontinence. Here we outline those we offer at Tennessee Valley Urology Center.
Stress incontinence
This is caused by sudden physical movements, such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, jumping, or lifting. Stress incontinence is a common following pregnancy or childbirth, menopause, surgical trauma, or pelvic radiation. It often occurs because of weakening or damage to the muscles that hold the urine in the bladder, such as the pelvic floor muscles and urethral sphincter.
Urge incontinence
Urgency is the symptom of a sudden need to urinate. People with urge incontinence experience a very sudden need to void and cannot make it to the bathroom in time. Urge incontinence usually results from overactivity of the detrusor muscles, which are part of the bladder wall and help it contract during urination.
Overflow incontinence
This issue occurs when a person is unable to completely empty the bladder by urinating and is associated with frequent uncontrolled leakage. The bladder becomes too full and as a result, urine “overflows” and incontinence occurs. It can be caused by an enlarged prostate, diabetes, spinal cord injuries or other neurological issues.
Mixed incontinence
This is when patients have a combination of both stress incontinence and urge incontinence. For many people, either urge or stress incontinence is often more bothersome than the other, but both can occur.
Diagnosing Urinary Incontinence
Diagnosing urinary incontinence primarily involves observing and recognising patterns. For example, a patient may fill out a bladder diary for three or more days with:
- Exact times of urination
- Volume of urination
- Volumes of fluid consumed
- Types of fluids consumed
A urologist may also ask questions about the patient’s symptoms and family history. These questions will not only identify the symptoms of urinary incontinence, they will also help rule out other possible reasons for the patient’s symptoms. A physical examination and other tests are important.

Physical examination
This may be a bit intimidating for the patient, especially those from culturally diverse backgrounds, but for the doctor, it is routine and normal. The simplest test will start with a request to remove clothing from the waist down. After this, the actions of the doctor will be determined by the patient’s gender.
Female patients
During the examination, the vagina will be examined for the presence of a cystocele, which is a bulge that comes from part of the bladder. The doctor may also test the strength of the pelvic floor muscle, which can be determined by asking the patient to cough and push down to assess for urine leakage.
Male patients
For males, the doctor may inspect the prostate gland, known clinically as a digital rectal examination. During this examination, a finger is inserted into the anus and the size of the prostate is estimated from the impression.

Urine Tests
A urine dipstick test is usually conducted to determine if the problem is related to a urinary tract infection. During this test, a sample of the patient’s urine is collected and a testing stick dipped into it. The stick changes color in the presence of bacteria, blood, and or protein in the urine.
A residual urine test can also be conducted to determine if the patient is emptying the bladder well. The objective with this test is to determine how much urine remains in the bladder after the patient voids. This can be determined using an ultrasound or by draining the contents with a catheter, which is a long flexible tube that is passed along the urethra into the bladder.
Next steps
Often, treatments can be prescribed after this stage. Even if the condition isn’t completely identified, a doctor may still prescribe treatment. If the treatment works, then it’s an effective way of confirming a diagnosis. However, if a patient isn’t improving, then further tests are available, such as:
- Cystoscopy, which is an explorative procedure that aims to spot problems inside the bladder and urinary tract that may have been missed in earlier tests
- Urodynamic tests, which seek to determine the pressure inside the bladder and rate of urine flow

